BM25Retriever原理
- 其中:
- 查询
- 查询
例子
处理文档
from haystack import Document
from haystack.components.retrievers.in_memory import InMemoryBM25Retriever
from haystack.document_stores.in_memory import InMemoryDocumentStore
document_store = InMemoryDocumentStore()
documents = [
Document(content="There are over 7,000 languages spoken around the world today."),
Document(content="Elephants have been observed to behave in a way that indicates
a high level of self-awareness, such as recognizing themselves in mirrors."),
Document(content="In certain parts of the world, like the Maldives, Puerto Rico,
and San Diego, you can witness the phenomenon of bioluminescent waves.")
]
document_store.write_documents(documents=documents)
处理查询
retriever = InMemoryBM25Retriever(document_store=document_store)
docs = retriever.run(query="How many languages are spoken around the world today?")["documents"]
for doc in docs:
print(f"content: {doc.content}")
print(f"score: {doc.score}")
输出
content: There are over 7,000 languages spoken around the world today.
score: 7.815769833242408
content: In certain parts of the world, like the Maldives, Puerto Rico, and San Diego,
you can witness the phenomenon of bioluminescent waves.
score: 4.314753296196667
content: Elephants have been observed to behave in a way that indicates a high level
of self-awareness, such as recognizing themselves in mirrors.
score: 3.652595952218814
优缺点
- 速度快:基于统计的分数计算公式很简单,可以快速处理大规模文本数据
- 存储开销小:除文本外无需存储额外数据。如果下游大模型通过API调用,rag不需要显卡也能跑起来,而且很快
- 太依赖关键字:query质量不高就搜不到,无法捕获文本的上下文语义信息。比如,在搜索引擎中,如果不输入关键字那必然搜不到我们想要的内容
BERT
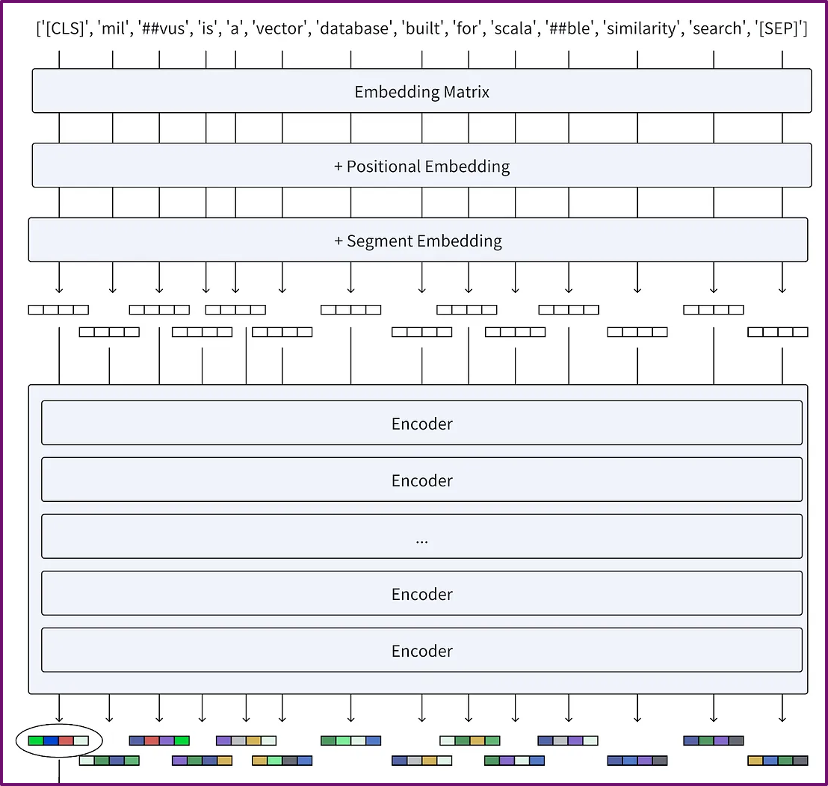
最近几年,一种基于BERT架构衍生出来的多种语义检索技术被更多地用到了RAG中,他是一种encoder-only的transformer架构:
- Tokenizer:words -> tokens
- Embedding:tokens -> vectors
- Encoder Stack:vectors -> vectors
简言之,它可以将文本转换成若干token vector
DenseEmbeddingRetriever: 文本嵌入模型
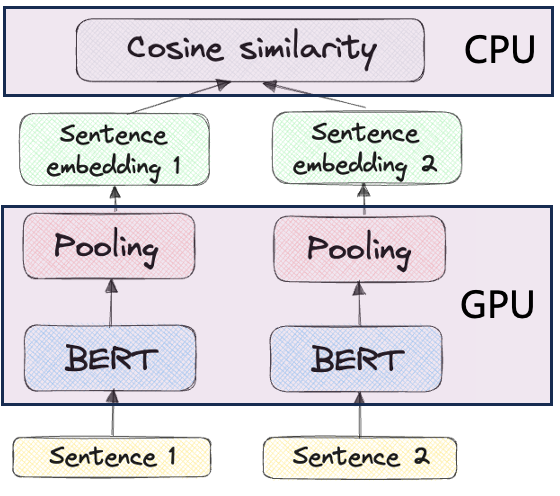
密集嵌入检索器基于双编码器(Bi-Encoder)架构,在BERT上面外加一层池化层(Pooling),得到单一的句向量,存储到document.embedding中。
- sentence ->BERT-Encoder -> token vectors
- token vectors -> Pooling Layer -> sentence vector
- score(SentenceA, SentenceB) = cosine_similarity(vectorA,vectorB)
DenseEmbeddingRetriever: 相似度计算
- 密集向量会交给一个经过训练的嵌入模型生成,它可以将相似的句子映射到高维空间中距离相近、方向相似的向量,常用的相似度分数计算公式有两种:
- 余弦相似度:常用的相似度计算公式,计算两个向量之间的夹角的余弦值。两个向量的方向越一致相似度越高
DenseEmbeddingRetriever: 相似度计算
- 欧式似度:直接计算两个向量之间的欧几里得距离,然后取个倒数得到相似度分数。也可以用其他距离:曼哈顿距离、汉明距离等
例子
- 模型: sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2, 22.7M params
- 相似度分数:余弦相似度
from haystack import Document, Pipeline
from haystack.document_stores.in_memory import InMemoryDocumentStore
from haystack.components.embedders import (
SentenceTransformersTextEmbedder,
SentenceTransformersDocumentEmbedder,
)
from haystack.components.retrievers import InMemoryEmbeddingRetriever
document_store = InMemoryDocumentStore(embedding_similarity_function="cosine")
documents = [
Document(content="There are over 7,000 languages spoken around the world today."),
Document(content="Elephants have been observed to behave in a way that indicates
a high level of self-awareness, such as recognizing themselves in mirrors."),
Document(content="In certain parts of the world, like the Maldives, Puerto Rico,
and San Diego, you can witness the phenomenon of bioluminescent waves."),
]
document_embedder = SentenceTransformersDocumentEmbedder(
model="sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2"
)
document_embedder.warm_up()
documents_with_embeddings = document_embedder.run(documents)["documents"]
document_store.write_documents(documents_with_embeddings)
for doc in documents_with_embeddings:
print(f"content: {doc.content}")
print(f"score: {doc.score}")
print(f"embedding: {doc.embedding}\n")
输出
content: There are over 7,000 languages spoken around the world today.
score: None
embedding: [0.03276507928967476, ..., 0.022160163149237633]
content: Elephants have been observed to behave in a way that indicates
a high level of self-awareness, such as recognizing themselves in mirrors.
score: None
embedding: [0.01985647901892662, ..., 0.007489172276109457]
content: In certain parts of the world, like the Maldives, Puerto Rico,
and San Diego, you can witness the phenomenon of bioluminescent waves.
score: None
embedding: [0.08535218983888626, ..., 0.013049677945673466]
处理查询
query_pipeline = Pipeline()
query_pipeline.add_component(
"text_embedder",
SentenceTransformersTextEmbedder(model="sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2"),
)
query_pipeline.add_component(
"retriever", InMemoryEmbeddingRetriever(document_store=document_store)
)
query_pipeline.connect("text_embedder.embedding", "retriever.query_embedding")
query = "How many languages are there?"
result = query_pipeline.run({"text_embedder": {"text": query}})
result_documents = result["retriever"]["documents"]
for doc in result_documents:
print(f"content: {doc.content}")
print(f"score: {doc.score}\n")
输出
content: There are over 7,000 languages spoken around the world today.
score: 0.7557791921810213
content: Elephants have been observed to behave in a way that indicates
a high level of self-awareness, such as recognizing themselves in mirrors.
score: 0.04221229572888512
content: In certain parts of the world, like the Maldives, Puerto Rico,
and San Diego, you can witness the phenomenon of bioluminescent waves.
score: -0.001667837080811814
优缺点
- 速度快:可以提前在GPU上计算并存储文档块的dense embedding,计算相似度就会很快
- 存储开销小:每个文档块只需要额外存储一个高维向量(通常768或1024维)
- 捕获句子的语义信息:只要是相似的句子,关键字不匹配也可以检索到
- 丢失词元信息:BERT产生的众多词元向量全部被映射到单一句向量,丢失了很多文本中的细节。快速地粗读文本,速度虽快但忽略了细节,只了解了个大概
SimilarityReranker: 相似度计算模型
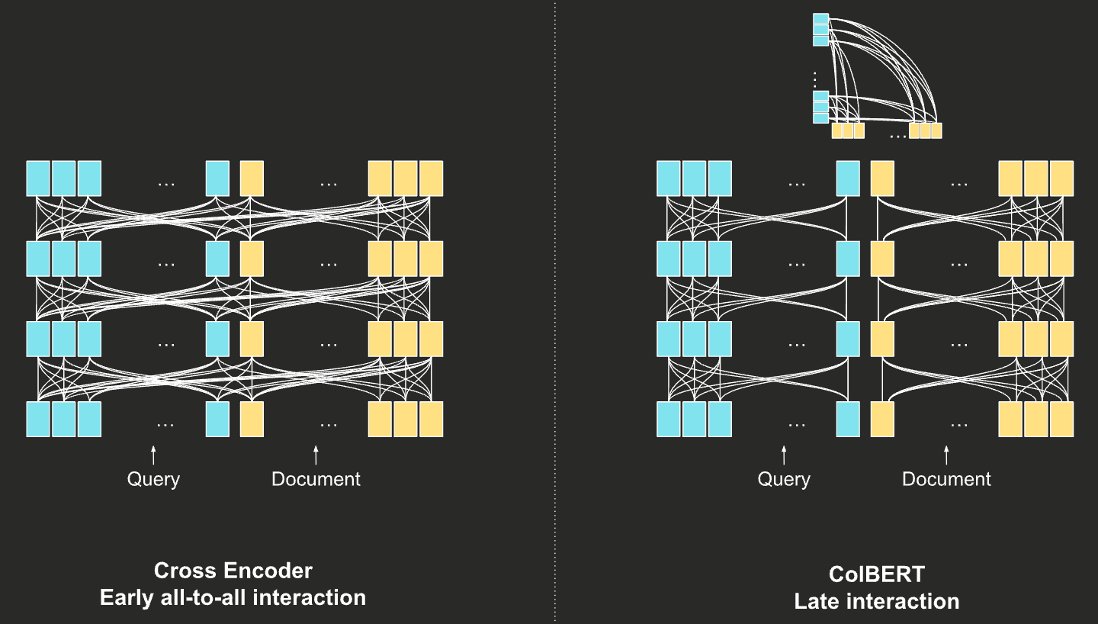
- similarity reranker基于交叉编码器(cross-encoder)架构
- 直接将两个句子串联起来,交给BERT,使得两个句子的词元向量可以在BERT内部相互交叉(cross)地进行交互,最终经过softmax得到一个相似度分数
SimilarityReranker: 相似度计算模型
- cross vs. colbert: 词元向量的交互从相似度计算阶段(colbert),提前到BERT模型内部(cross)
例子
from haystack import Document
from haystack.components.rankers import TransformersSimilarityRanker
documents = [
Document(content="There are over 7,000 languages spoken around the world today."),
Document(content="Elephants have been observed to behave in a way that indicates
a high level of self-awareness, such as recognizing themselves in mirrors."),
Document(content="In certain parts of the world, like the Maldives, Puerto Rico,
and San Diego, you can witness the phenomenon of bioluminescent waves."),
]
ranker = TransformersSimilarityRanker(model="cross-encoder/ms-marco-MiniLM-L-6-v2")
ranker.warm_up()
query = "How many languages are there?"
ranked_documents = ranker.run(query=query, documents=documents)["documents"]
for doc in ranked_documents:
print(f"content: {doc.content}")
print(f"score: {doc.score}\n")
输出
content: There are over 7,000 languages spoken around the world today.
score: 0.9998884201049805
content: Elephants have been observed to behave in a way that indicates
a high level of self-awareness, such as recognizing themselves in mirrors.
score: 1.4616251974075567e-05
content: In certain parts of the world, like the Maldives, Puerto Rico,
and San Diego, you can witness the phenomenon of bioluminescent waves.
score: 1.4220857337932102e-05
优缺点
- 充分利用词元信息:相似度直接在模型内部完成计算。同时看两个文本,交叉理解两个文本的单词的含义,训练好的模型可以得到很好的相似度计算结果
- 在线计算:所有的计算都要在GPU上在线完成,无法提前存储一些信息,实现之前的离线计算,因此会很慢
Simple RAG
挑一种文档划分方法,再挑一个检索器,一个简单的RAG就可以完成了
from prompt_toolkit import prompt
from haystack import Pipeline
from haystack.utils import Secret
from haystack.document_stores.in_memory import InMemoryDocumentStore
from haystack.components.fetchers import LinkContentFetcher
from haystack.components.converters import HTMLToDocument
from haystack.components.preprocessors import DocumentSplitter
from haystack.components.writers import DocumentWriter
from haystack.components.retrievers.in_memory import InMemoryEmbeddingRetriever
from haystack.components.generators import OpenAIGenerator
from haystack.components.builders.prompt_builder import PromptBuilder
from haystack.components.embedders import (
SentenceTransformersTextEmbedder, SentenceTransformersDocumentEmbedder,)
处理文档
- 使用sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2嵌入模型进行检索
- 以3行为单位进行切分,并且有1行的overlap
- 将南京大学的wiki网页作为知识库:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nanjing_University
处理文档
document_store = InMemoryDocumentStore()
fetcher = LinkContentFetcher()
converter = HTMLToDocument()
splitter = DocumentSplitter(split_by="sentence", split_length=3, split_overlap=1)
document_embedder = SentenceTransformersDocumentEmbedder(
model="sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2"
)
writer = DocumentWriter(document_store = document_store)
indexing_pipeline = Pipeline()
indexing_pipeline.add_component("fetcher", fetcher)
indexing_pipeline.add_component("converter", converter)
indexing_pipeline.add_component("splitter", splitter)
indexing_pipeline.add_component("document_embedder", document_embedder)
indexing_pipeline.add_component("writer", writer)
indexing_pipeline.connect("fetcher.streams", "converter.sources")
indexing_pipeline.connect("converter.documents", "splitter.documents")
indexing_pipeline.connect("splitter.documents", "document_embedder.documents")
indexing_pipeline.connect("document_embedder.documents", "writer.documents")
indexing_pipeline.run(data={"fetcher": {"urls": ["https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nanjing_University"]}})
处理查询
prompt_template = """
Given these documents, answer the question.
Documents:
{% for doc in documents %}
{{ doc.content }}
{% endfor %}
Question: {{question}}
Answer:
"""
api_key = "xxx"
model = "gpt-4o-mini"
api_base_url = None
query_embedder = SentenceTransformersTextEmbedder(model="sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2")
retriever = InMemoryEmbeddingRetriever(document_store=document_store)
prompt_builder = PromptBuilder(template=prompt_template)
llm = OpenAIGenerator(
api_key=Secret.from_token(api_key),
model=model,
api_base_url=api_base_url
)
处理查询
rag_pipeline = Pipeline()
rag_pipeline.add_component("query_embedder", query_embedder)
rag_pipeline.add_component("retriever", retriever)
rag_pipeline.add_component("prompt_builder", prompt_builder)
rag_pipeline.add_component("llm", llm)
rag_pipeline.connect("query_embedder.embedding", "retriever.query_embedding")
rag_pipeline.connect("retriever.documents", "prompt_builder.documents")
rag_pipeline.connect("prompt_builder.prompt", "llm.prompt")
while(True):
question = prompt("> ")
results = rag_pipeline.run(
{
"query_embedder": {"text": question},
"prompt_builder": {"question": question},
}
)
reply = results["llm"]["replies"][0]
print(reply)
测试
What is the motto of Nanjing University?
The motto of Nanjing University is "诚朴雄伟励学敦行," which translates to "Sincerity with Aspiration, Perseverance and Integrity" in English. The first half of this motto was the motto during the National Central University time, and the last half was quoted from the classic literature work Book of Rites.
What is the song of Nanjing University?
The song of Nanjing University is the university song, which was created in 1916. It is the first school song in the modern history of Nanjing University. The lyrics were written by Jiang Qian, and the melody was composed by Li Shutong. The song was recovered in 2002.
问一些大模型不知道的问题
question: Who is the modern China's first PhD in Chinese Language and Literature?
Chatgpt answer
- 一会说1986年的郭齐勇,一会说1983年的陈平原
RAG answer
The modern China's first PhD in Chinese Language and Literature is Mo Lifeng (莫砺锋), as mentioned in the documents.

Advanced RAG: 检索结果合并
- 不同的检索器有不同的侧重点,会得到不同的相似度分数分布,如何综合考虑?例如一本书我既想略读整体(dense embedding),也想跳着读重点部分(sparse embedding)
- 权重合并(Weight Merge)
- 两种检索机制的分数的值域、分布不一致,通过放缩补偿
- 通过加权和计算综合分数
Advanced RAG: 检索结果合并
- RRF(倒排融合)
- 只考虑文档在排序中的位置,忽略分数分布
例子
import
from haystack import Document, Pipeline
from haystack.document_stores.in_memory import InMemoryDocumentStore
from haystack.components.embedders import (
SentenceTransformersTextEmbedder,
SentenceTransformersDocumentEmbedder,
)
from haystack.components.retrievers.in_memory import InMemoryBM25Retriever
from haystack.components.retrievers import InMemoryEmbeddingRetriever
from haystack.components.joiners.document_joiner import DocumentJoiner
文档处理
document_store = InMemoryDocumentStore(embedding_similarity_function="cosine")
query = "What are effective strategies to improve English speaking skills?"
documents = [
Document(content="Practicing with native speakers enhances English
speaking proficiency."),
Document(content="Regular participation in debates and discussions
refine public speaking skills in English."),
Document(content="Studying the history of the English language does
not directly improve speaking skills."),
]
document_embedder = SentenceTransformersDocumentEmbedder(
model="sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2"
)
document_embedder.warm_up()
documents_with_embeddings = document_embedder.run(documents)["documents"]
document_store.write_documents(documents_with_embeddings)
bm25检索
bm25_retriever = InMemoryBM25Retriever(document_store=document_store,scale_score=True)
bm25_docs = bm25_retriever.run(query=query)["documents"]
print("bm25:")
for doc in bm25_docs:
print(f"content: {doc.content}")
print(f"score: {doc.score}\n")
输出
content: Studying the history of the English language does not directly improve
speaking skills.
score: 0.5593245377361279
content: Regular participation in debates and discussions refine public speaking
skills in English.
score: 0.545159185512614
content: Practicing with native speakers enhances English speaking proficiency.
score: 0.5387709786621966
dense embedding检索
query_pipeline = Pipeline()
query_pipeline.add_component(
"text_embedder",
SentenceTransformersTextEmbedder(model="sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2"),
)
query_pipeline.add_component(
"dense_retriever", InMemoryEmbeddingRetriever(document_store=document_store,scale_score=True)
)
query_pipeline.connect("text_embedder.embedding", "dense_retriever.query_embedding")
dense_docs = query_pipeline.run({"text_embedder": {"text": query}})["dense_retriever"]["documents"]
print("dense:")
for doc in dense_docs:
print(f"content: {doc.content}")
print(f"score: {doc.score}\n")
输出
content: Practicing with native speakers enhances English speaking proficiency.
score: 0.8296398226909952
content: Regular participation in debates and discussions refine public speaking
skills in English.
score: 0.8017774366152697
content: Studying the history of the English language does not directly improve
speaking skills.
score: 0.7334273104138469
权重合并
joiner = DocumentJoiner(join_mode="merge", weights=[0.3, 0.7])
merge_docs = joiner.run(documents=[bm25_docs, dense_docs])["documents"]
for doc in merge_docs:
print(f"content: {doc.content}")
print(f"score: {doc.score}\n")
输出
content: Practicing with native speakers enhances English speaking proficiency.
score: 0.7423791694823556
content: Regular participation in debates and discussions refine public speaking
skills in English.
score: 0.724791961284473
content: Studying the history of the English language does not directly improve
speaking skills.
score: 0.6811964786105311
RRF合并
joiner = DocumentJoiner(join_mode="reciprocal_rank_fusion")
rrf_docs = joiner.run(documents=[bm25_docs,dense_docs])["documents"]
print("rrf:")
for doc in rrf_docs:
print(f"content: {doc.content}")
print(f"score: {doc.score}\n")
输出
content: Studying the history of the English language does not directly improve speaking skills.
score: 0.9841269841269842
content: Practicing with native speakers enhances English
speaking proficiency.
score: 0.9841269841269842
content: Regular participation in debates and discussions refine public speaking
skills in English.
score: 0.9838709677419354
RRF计算:haystack使用k=61,并且进行了额外的放缩处理,
- Studying...:bm25的排序为1,dense的排序为3,因此:
- Practicing...:bm25的排序为3,dense的排序为1,因此:
- Regular...:bm25的排序为3,dense的排序为1,因此:
重排序机制
- 有些检索器速度快但效果不好(dense,sparse,bm25),有些检索器速度慢但效果好(colbert,cross)
- 可以先用速度快的检索器先网罗一批候选文档,再用效果好的检索器重新排序。先快速粗读所有文档,找出一批看起来不错的文档,再精读候选文档,找出质量好的
例子
import
from haystack import Document
from haystack.document_stores.in_memory import InMemoryDocumentStore
from haystack.components.retrievers.in_memory import InMemoryBM25Retriever
from haystack.components.rankers import TransformersSimilarityRanker
文档处理
query = "What are effective strategies to improve English speaking skills?"
documents = [
Document(
content="Practicing with native speakers enhances English speaking proficiency."
),
Document(
content="Daily vocabulary expansion is crucial for improving oral communication skills."
),
Document(
content="Engaging in language exchange programs can significantly boost speaking abilities."
),
Document(
content="Regular participation in debates and discussions refine public speaking skills in English."
),
Document(
content="Studying the history of the English language does not directly improve speaking skills."
),
]
document_store = InMemoryDocumentStore()
document_store.write_documents(documents)
bm25初步检索
bm25_retriever = InMemoryBM25Retriever(document_store=document_store)
bm25_docs = bm25_retriever.run(query=query, top_k=4)["documents"]
print("bm25:")
for doc in bm25_docs:
print(f"content: {doc.content}")
print(f"score: {doc.score}\n")
输出
bm25:
content: Studying the history of the English language does not directly improve speaking skills.
score: 3.1117211646172698
content: Regular participation in debates and discussions refine public speaking skills in English.
score: 2.443788686074245
content: Practicing with native speakers enhances English speaking proficiency.
score: 2.2622329312889553
content: Daily vocabulary expansion is crucial for improving oral communication skills.
score: 2.0359854825047066
重排序
reranker = TransformersSimilarityRanker(model="cross-encoder/ms-marco-MiniLM-L-6-v2")
reranker.warm_up()
reranked_docs = reranker.run(query=query, documents=bm25_docs, top_k=3)["documents"]
print("reranker:")
for doc in reranked_docs:
print(f"content: {doc.content}")
print(f"score: {doc.score}\n")
输出
reranker:
content: Practicing with native speakers enhances English speaking proficiency.
score: 0.769904375076294
content: Studying the history of the English language does not directly improve
speaking skills.
score: 0.5486361384391785
content: Daily vocabulary expansion is crucial for improving oral communication
skills.
score: 0.3509156107902527
上下文丰富
小文档块的检索准确度更高,但丢失了更多上下文信息,因此可以在检索后丰富上下文来补偿
上下文窗口扩展(Sentence window retrieval)
- 以小文档块为单位进行检索可以保证检索准确度,和相邻若干文档块合并形成大文档块可以保证信息量
- 翻阅书本时,突然扫到了重点,会下意识联系上下文看一看,看有没有额外的相关信息可以参考
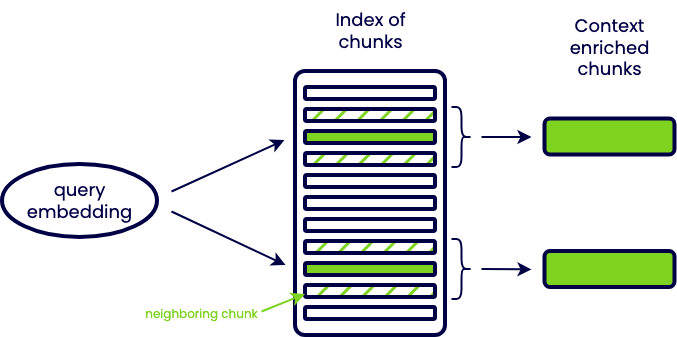
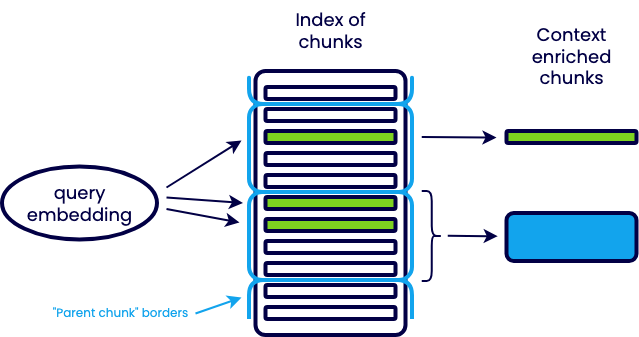
自动合并检索(Auto-merging retrieval)
- 任何时候都进行上下文扩展并不合理,当检索命中的小文档块数量在大文档块中的占比达到一定阈值时(例如50%),才进行合并
- 翻阅书本时,发现重点都聚集在某一章节,那这一章节可能都很重要