举个例子
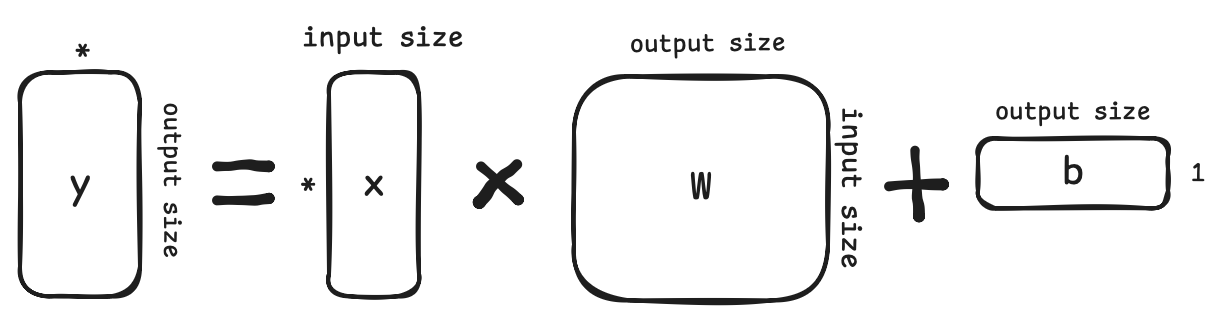
linear = nn.Linear(5,3)
print(linear.weight.shape, linear.bias.shape)
举个例子
-
torch.matmal, @
-
torch.add, +
-
移步vscode,试一试,shape那些事,以及Tensor Broadcasting
Tensor Broadcasting
试试这段代码
a = torch.randn(2, 2, 4)
print(a)
b = 20
a = a + b
print(a)
c = torch.randn(2,4)
a = a + c
print(c)
print(a)
Tensor Broadcasting
并行运算在深度学习时代非常重要
- N个样本,每个样本的shape (2, 4), 模型参数(2, 4)
- 一个batch的输入通常的shape (2, 2, 4)
- 如何为这个batch批量执行每个样本和模型参数的计算?
- 比如:
- Tensor 1 (2, 2, 4) * Tensor 2 (2, 4)
- Tensor 1 (2, 2, 4) @ Tensor 2 (4, 2)
- 比如:
Tensor Broadcasting的原则
- Each tensor must have at least one dimension - no empty tensors.
- Comparing the dimension sizes of the two tensors, going from last to first:
- Each dimension must be equal, or
- One of the dimensions must be of size 1, or
- The dimension does not exist in one of the tensors
模型结构中一些重要的函数
-
nn.functional
-
激活函数(引入非线性)
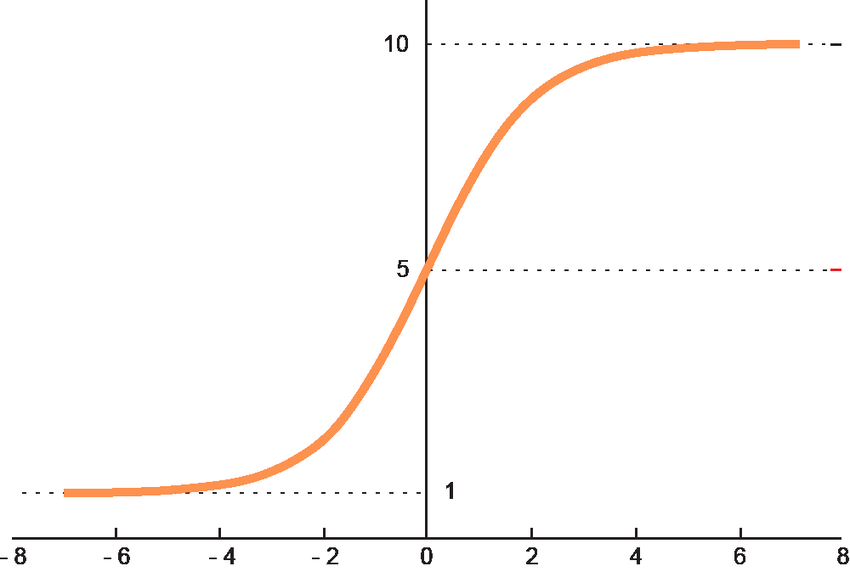
- relu, sigmoid
-
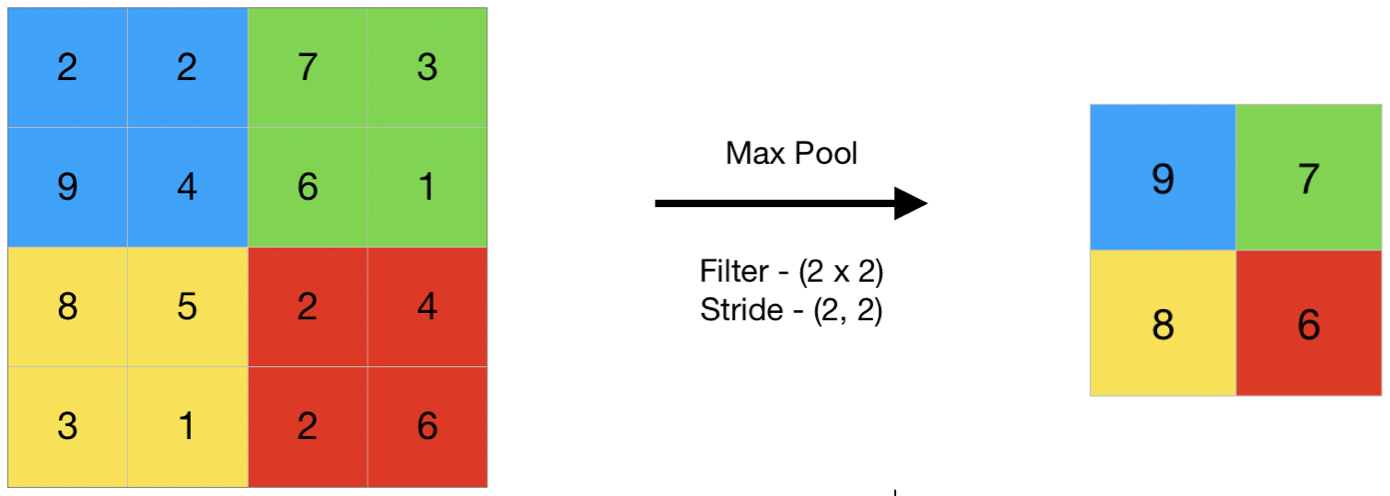
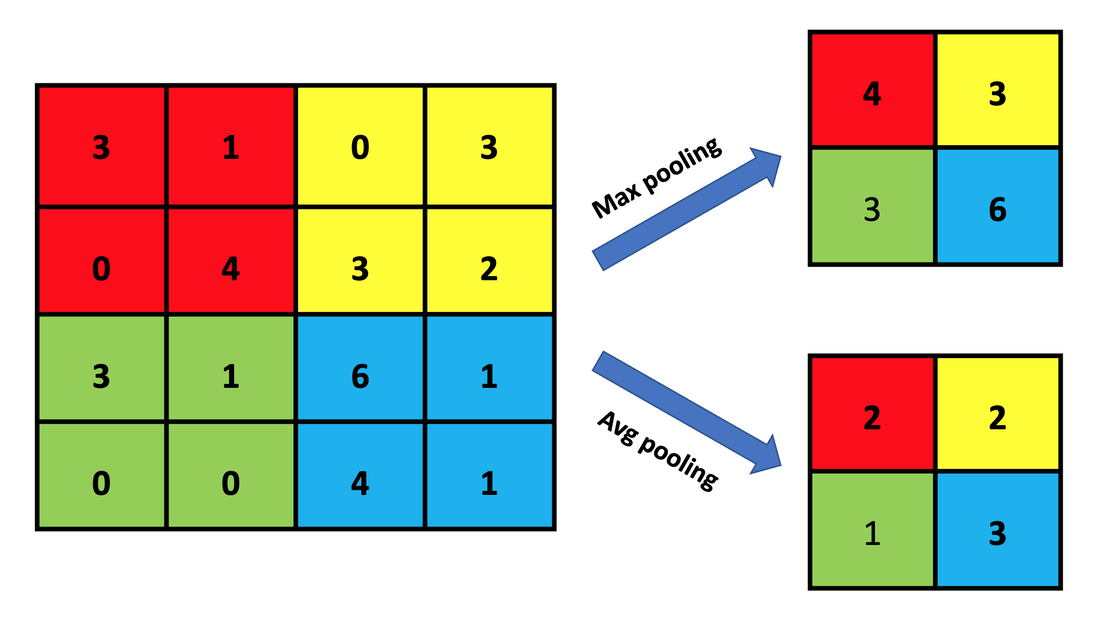
池化
- average pooling, max pooling
- 1d, 2d, ...
- average pooling, max pooling
激活函数(引入非线性)
- 通过引入非线性函数(nonlinear function)可增加模型非线性的能力,在模型中中,也称之为激活函数
- 线性层:
- 激活:
- 线性层:
- activation类型
- ReLU, Sigmoid, SwiGLU, ...
激活函数(引入非线性)
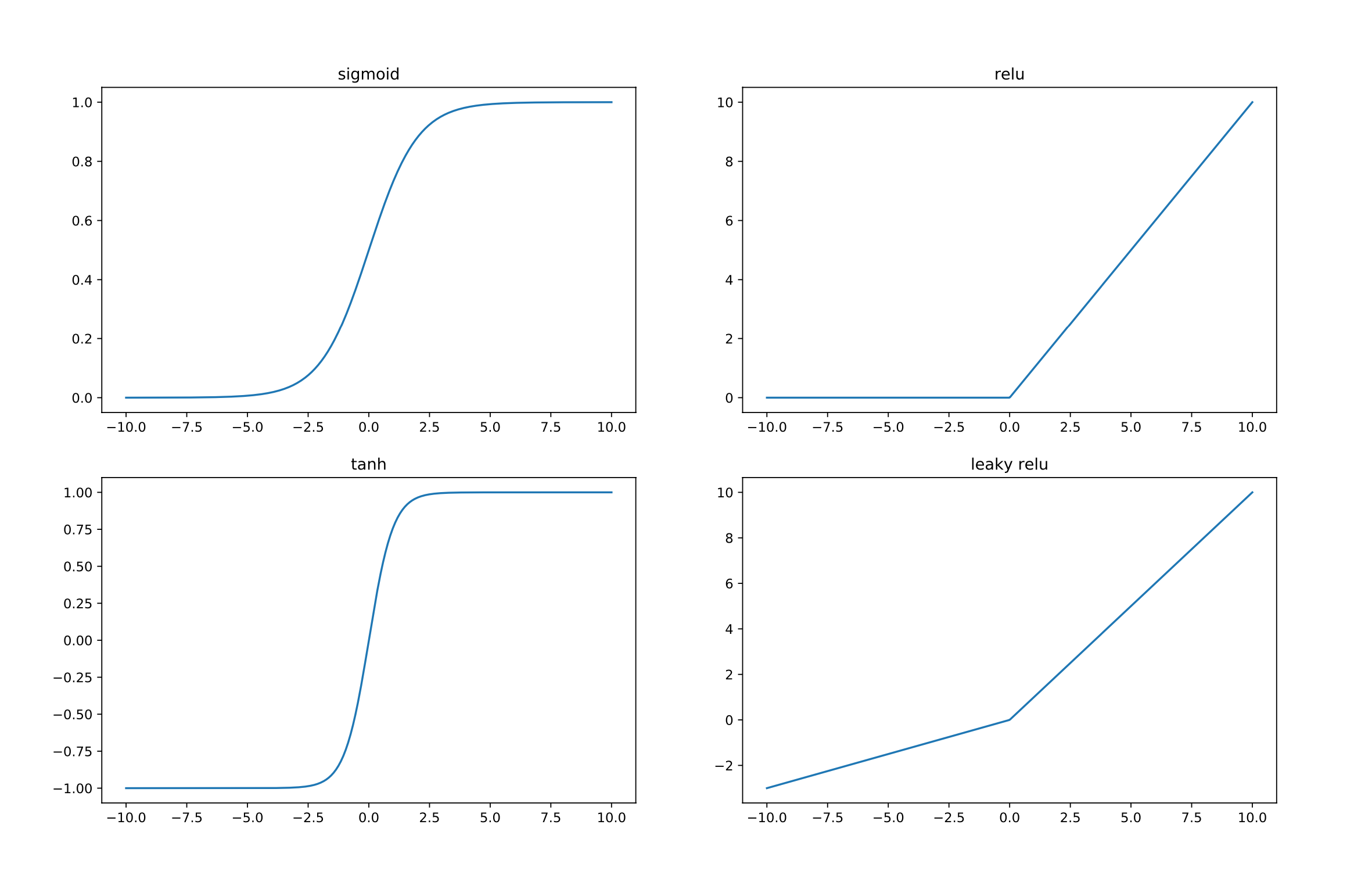
激活函数(引入非线性)
池化 (pooling)
池化: “粗暴的”降维方法

池化 (pooling)
池化: “粗暴的”降维方法
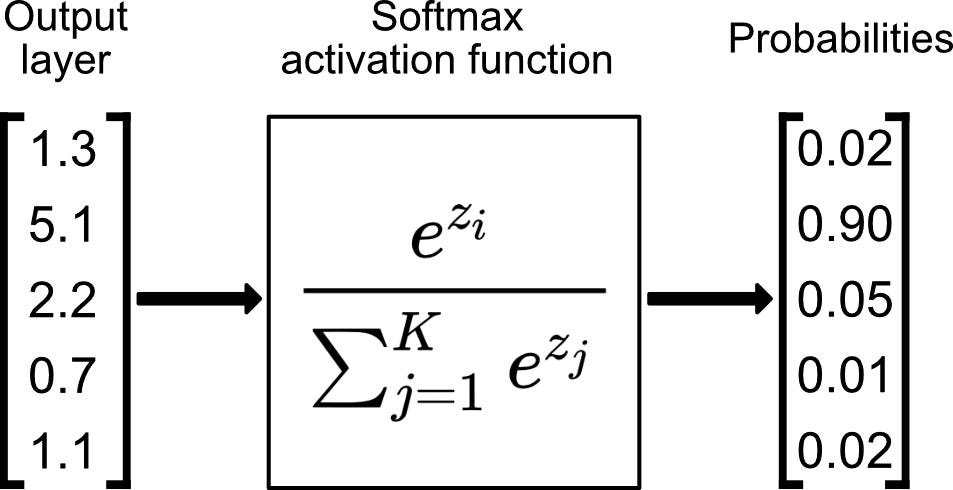
模型的最终输出
以分类问题举例
- 对于多分类问题而言,假设
- 其中,
softmax示例及可视化
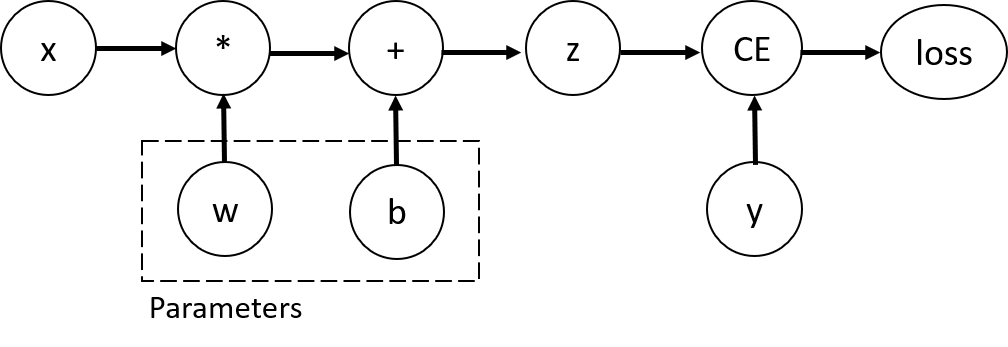
回顾模型结构: Forward干了些什么事
- 构建模型的推理(inference)过程:计算图
def forward(self, x):
x = nn.functional.relu(self.conv1(x))
x = nn.functional.max_pool2d(x, 2, 2)
x = nn.functional.relu(self.conv2(x))
x = nn.functional.max_pool2d(x, 2, 2)
x = x.view(-1, 16*4*4)
x = nn.functional.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = nn.functional.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
计算图示例
x = torch.ones(5) # input tensor
y = torch.zeros(3) # expected output
w = torch.randn(5, 3, requires_grad=True)
b = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
z = torch.matmul(x, w)+b
loss = torch.nn.functional.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(z, y)
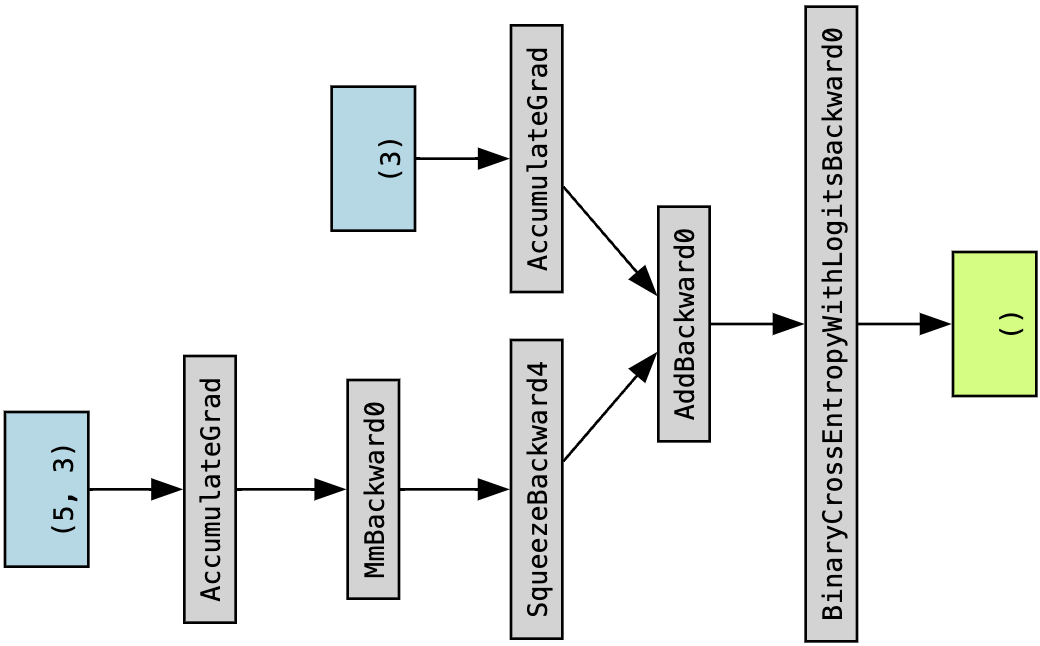
计算图示例: torchviz展示
模型的训练/学习
- 假设,构建模型
- 目标: 设计一种可用来度量基于
- 学习方法:梯度下降,寻找合适的
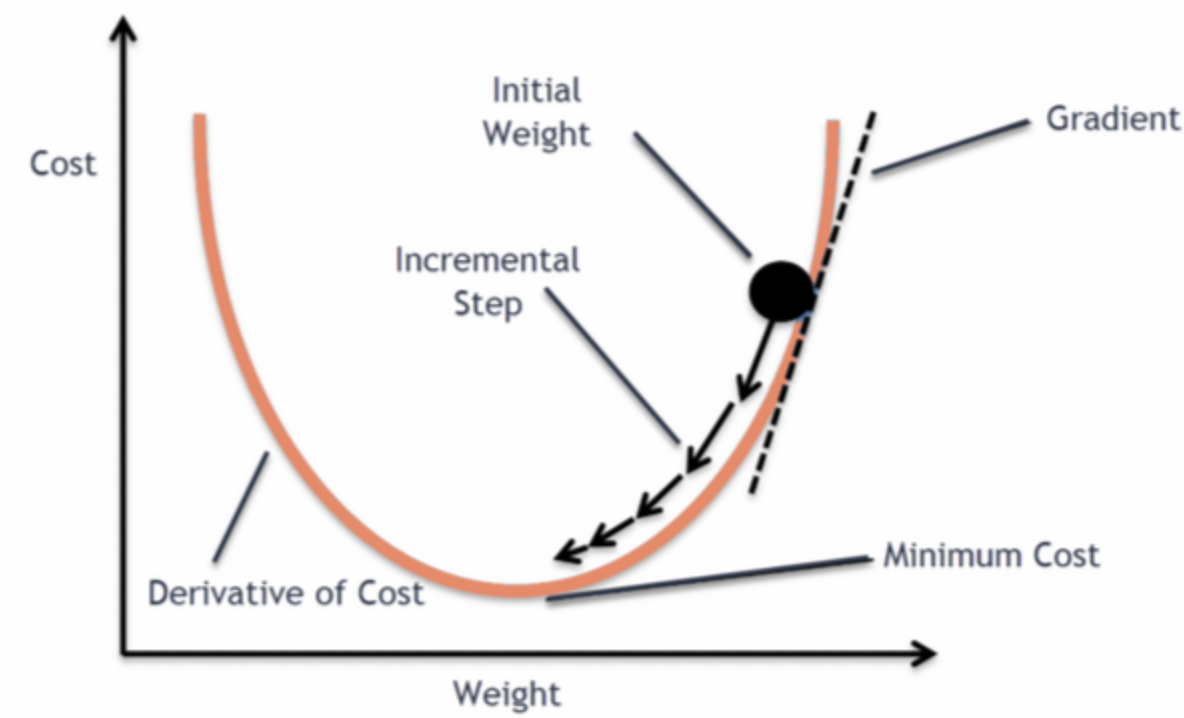
模型的训练/学习
- 目标:
- 猜个
- 评估误差:
- 根据误差,更新

训练模型(参数)
优化目标:
梯度下降法 (Gradient descent): 求偏导
-
- 通常深度学习模型
-
核心算法: 反向传播(backpropagation)
- 核心步骤: 针对优化目标
- 核心步骤: 针对优化目标
反向传播(backpropagation)
-
假设深度学习模型为
-
优化目标
-
链式法则展开:
-
偏导的构建
- 传统手工实现 v.s. autograd
Autograd
-
“古代”手工实现
- forward: 代码实现
- backward: 手推偏导公式
- forward: 代码实现
-
autograd
- forward: 基于forward实现构建计算图
- backward: 基于计算图实现自动微分(automatic differentiation)
Autograd深入理解
参考阅读
模型的训练/学习
目标:
- 猜个
- 评估误差:
- 根据误差,更新

模型的训练/学习的实现
定义损失函数(loss),以及优化器(优化算法)
ce_loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
-
常见损失函数,可在torch.nn中调用
- nn.CrossEntropyLoss, nn.L1Loss, nn.MSELoss, nn.NLLLoss, nn.KLDivLoss, nn.BCELoss, ...
-
常见优化算法,可在torch.optim中调用
- optim.SGD, optim.Adam, optim.AdamW, optim.LBFGS, ...
训练流程
def train(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
size = len(dataloader.dataset)
model.train()
for batch, (X, y) in enumerate(dataloader):
pred = model(X)
l = loss_fn(pred, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
l.backward()
optimizer.step()
if batch % 100 == 0:
loss, current = l.item(), batch * len(X)
print(f"loss: {loss:>7f} [{current:>5d}/{size:>5d}]")
测试流程
def test(dataloader, model, loss_fn):
size = len(dataloader.dataset)
num_batches = len(dataloader)
model.eval()
test_loss, correct = 0, 0
with torch.no_grad():
for X, y in dataloader:
pred = model(X)
test_loss += loss_fn(pred, y).item()
correct += (pred.argmax(1) == y).type(torch.float).sum().item()
test_loss /= num_batches
correct /= size
print(f"Test Error: \n Accuracy: {(100*correct):>0.1f}%, Avg loss: {test_loss:>8f} \n")
return correct